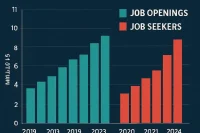
OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble as technology giants continue to recycle capital and artificially inflate valuations in the artificial intelligence sector. This pattern mirrors historical economic cycles where excessive investment flows create unsustainable market conditions that eventually lead to significant corrections. The current AI investment frenzy has raised legitimate concerns among economists and market analysts about the sustainability of current valuations and the potential for a major market correction.
The investment loop phenomenon occurs when large technology companies invest heavily in AI startups and technologies, which then use that capital to purchase services from the same companies, creating a circular flow of money that inflates valuations without generating genuine economic value. This pattern has become particularly evident in the OpenAI ecosystem, where Microsoft’s massive investments in OpenAI have created a feedback loop that benefits both companies while potentially masking underlying economic weaknesses.
The Gold Market Parallel: Economic Uncertainty Indicators
Similar patterns exist between AI investment concerns and how gold prices often signal broader economic concerns. The recent surge in gold prices reflects underlying economic uncertainty and inflation concerns that parallel the AI investment bubble fears. When investors lose confidence in traditional financial instruments and economic stability, they often turn to gold as a safe haven, just as they might turn to AI investments during periods of technological uncertainty.
The gold market analysis reveals several concerning patterns that mirror the AI investment landscape. Central banks are increasingly purchasing gold as a hedge against potential asset confiscation and currency devaluation, similar to how technology companies are hoarding AI investments as protection against competitive disruption. This defensive positioning suggests that both markets are experiencing similar underlying concerns about economic stability and future value preservation.
The correlation between gold prices and AI investment patterns becomes particularly evident when examining the timing of major market movements. Both sectors tend to experience significant volatility during periods of economic uncertainty, with investors seeking alternative stores of value when traditional markets appear unstable.
The Laffer Curve Connection: Tax Policy and Investment Flows
Current tax policies may be inadvertently encouraging excessive investment in AI technologies, contributing to bubble concerns. The Laffer Curve principle suggests that optimal tax rates can actually increase government revenue while stimulating economic growth, but when tax policies create artificial incentives for specific types of investments, they can distort market signals and lead to inefficient capital allocation.
The current tax environment provides significant incentives for technology investments, including research and development credits, accelerated depreciation schedules, and various investment tax credits. While these policies are designed to encourage innovation, they may be creating artificial demand for AI investments that doesn’t reflect genuine market needs or economic value creation.
The 50th anniversary of the Laffer Curve serves as a reminder that sound economic policy requires careful balance between encouraging growth and preventing market distortions. The current AI investment boom may represent a case where well-intentioned policies have created unintended consequences in the form of investment bubbles and capital misallocation.
Central Bank Behavior: Defensive Positioning Strategies
Central banks are engaging in defensive positioning strategies that mirror the AI investment patterns, creating similar concerns about market stability. Central banks are increasingly diversifying their reserves away from traditional currencies and into alternative assets like gold, reflecting concerns about currency stability and potential asset confiscation.
This defensive positioning creates a feedback loop similar to the AI investment cycle. As central banks move away from traditional reserve currencies, they create additional demand for alternative assets, which drives up prices and attracts more investors to these markets. This pattern can create self-reinforcing cycles that lead to asset bubbles and eventual market corrections.
The European Union’s control over Russian central bank reserves illustrates how geopolitical tensions can accelerate these defensive positioning strategies. When countries face potential asset freezes or confiscation, they naturally seek alternative stores of value, creating additional demand for both gold and AI investments as hedges against traditional financial system risks.
Inflation Concerns and Interest Rate Policy
Current inflation levels remain above target while there’s significant pressure to cut interest rates, creating conditions conducive to investment bubbles. This creates a dangerous combination of loose monetary policy and persistent inflation that historically leads to asset bubbles and eventual market corrections.
The Federal Reserve’s current position of maintaining interest rates while inflation remains above the 2% target creates an environment where investors seek higher returns through alternative investments like AI technologies. This search for yield in a low-interest-rate environment can drive excessive investment in speculative technologies and create unsustainable valuation bubbles.
The supply-side economics perspective suggests that proper economic growth through tax cuts, deregulation, and pro-production policies can actually reduce inflation by increasing supply and lowering costs. However, when monetary policy remains loose during periods of supply-side growth, it can create conditions where both inflation and asset bubbles develop simultaneously.
The Dollar’s Role in Global Investment Flows
The dollar’s position as the world’s reserve currency creates unique dynamics in global investment flows that can influence AI investment patterns. A strong, stable dollar typically attracts global capital and reduces the appeal of alternative investments like gold and speculative technologies. However, when the dollar weakens or becomes unstable, it drives capital toward alternative assets and creates conditions conducive to investment bubbles.
The “King Dollar” policy approach emphasizes maintaining a strong, stable, and reliable dollar that attracts global investment and provides a foundation for sustainable economic growth. This approach contrasts with policies that seek to weaken the dollar for competitive advantages, which can create instability and drive capital toward alternative investments.
The global race for capital has intensified as countries compete for investment flows, with the United States maintaining advantages through tax cuts, deregulation, and pro-business policies. However, maintaining these advantages requires consistent policy implementation and a stable monetary environment that doesn’t encourage excessive speculation in alternative assets.
Global Capital and the Dollar
The dollar’s role in global investment flows shapes everything from AI funding to market stability. Employers can stay competitive by hiring finance, economics, and policy experts who understand how currency strength impacts global capital movement. Post your job on WhatJobs today and connect with professionals ready to guide your organization in a shifting monetary landscape.
Post a Job Free for 30 Days →Peace and Stability: The Ultimate Economic Foundation
Geopolitical stability plays a crucial role in determining investment patterns and market stability across all sectors. The prospect of peace in the Middle East and resolution of the Russia-Ukraine conflict could significantly impact both gold prices and AI investment flows by reducing uncertainty and improving global economic conditions.
Peace and stability create conditions where investors feel confident in traditional financial instruments and long-term economic growth, reducing the appeal of alternative investments and speculative technologies. This stability allows for more rational capital allocation and reduces the likelihood of investment bubbles in any particular sector.
The current geopolitical environment, with potential for peace negotiations and conflict resolution, could create a shift away from defensive investments like gold and speculative investments like AI technologies toward more traditional growth-oriented investments that benefit from global stability and economic cooperation.
Market Psychology and Investment Behavior
Market psychology plays a crucial role in determining investment patterns and asset valuations across all sectors. When investors become fearful of traditional markets or uncertain about economic conditions, they often seek alternative investments that promise higher returns or protection against market volatility.
The AI investment boom has attracted significant attention from both institutional and individual investors seeking exposure to what appears to be the next major technological revolution. However, this enthusiasm can create conditions where valuations become disconnected from fundamental economic value, leading to the formation of investment bubbles.
The gold market’s historical role as a “first refuge of the cautious” provides insight into how investors behave during periods of uncertainty. When economic problems arise, investors naturally seek safe haven assets, but when this behavior becomes excessive or based on unfounded fears, it can create its own market distortions and eventual corrections.
Regulatory Environment and Market Oversight
The current regulatory environment may not be adequately addressing the unique challenges posed by AI investments and their potential for creating market distortions. Traditional financial regulations were designed for more conventional investment vehicles and may not effectively address the risks associated with AI investment cycles.
The need for appropriate regulatory oversight becomes particularly important when investment flows create feedback loops that can mask underlying economic weaknesses. Without proper oversight, these cycles can continue to inflate until they reach unsustainable levels and eventually collapse, causing significant economic damage.
The balance between encouraging innovation and preventing market manipulation requires careful regulatory design that addresses the unique characteristics of AI investments while maintaining market integrity and protecting investors from excessive risk.
The Future of AI Investment and Market Stability
The long-term sustainability of current AI investment patterns remains uncertain, raising important questions about market stability. While AI technologies hold significant promise for economic growth and productivity improvements, the current investment environment may be creating conditions that are unsustainable in the long term.
The key to preventing an AI investment bubble lies in ensuring that investment flows are based on genuine economic value creation rather than circular capital flows and artificial valuation inflation. This requires both market discipline and appropriate regulatory oversight to maintain healthy investment patterns.
The ultimate goal should be creating an environment where AI investments contribute to genuine economic growth and productivity improvements while avoiding the speculative excesses that characterize investment bubbles. This requires careful balance between encouraging innovation and maintaining market stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble mean for investors?
OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble means that circular investment patterns between tech giants and AI companies may be artificially inflating valuations and creating unsustainable market conditions that could lead to significant corrections and investment losses.
How does OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble compare to historical market cycles?
OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble shows similar patterns to previous market cycles like the dotcom bubble, where excessive investment flows and circular capital movements created unsustainable valuations that eventually led to major market corrections and economic disruption.
What are the warning signs that OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble?
Warning signs include circular investment flows between related companies, valuations disconnected from fundamental economic value, excessive enthusiasm from both institutional and individual investors, and regulatory oversight that may not adequately address the unique risks of AI investment cycles.
How can investors protect themselves from OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble?
Investors can protect themselves by focusing on companies with genuine economic value creation, diversifying across different sectors and investment types, maintaining a long-term perspective, and avoiding investments based primarily on hype or circular capital flows rather than fundamental business performance.
A Real-World Example: Sarah’s Investment Dilemma
Sarah Rodriguez, a 32-year-old investment analyst from Chicago, exemplifies how OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble can impact individual investment decisions. After witnessing the dotcom crash as a teenager, Sarah was initially excited about AI investment opportunities but became increasingly concerned about the circular investment patterns she observed.
“I started noticing that many AI companies were essentially trading money back and forth with their major investors,” Sarah explains. “When I analyzed the cash flows, it became clear that a significant portion of the ‘growth’ was actually just circular capital movements rather than genuine economic value creation.”
Sarah’s analysis revealed that OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble because the investment patterns she observed mirrored those that preceded previous market crashes. She noticed that valuations were increasingly based on investment flows rather than fundamental business performance, and that many companies were using investor capital to purchase services from their own investors.
“OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble taught me to look beyond surface-level metrics and examine the underlying economic fundamentals,” Sarah says. “The key was identifying whether companies were creating genuine value or just participating in circular capital flows that artificially inflated their valuations.”
Through her careful analysis of OpenAI investment loop creates fear of an AI bubble patterns, Sarah was able to adjust her investment strategy to focus on companies with sustainable business models and genuine value creation, while avoiding those that appeared to be primarily benefiting from circular investment flows. Her experience demonstrates the importance of fundamental analysis in navigating complex investment environments.